 Applications for the sandwich undergraduate program in France for students of Electronics Engineering and Electrical Engineering at UFSC are open until March 16, 2025.
Applications for the sandwich undergraduate program in France for students of Electronics Engineering and Electrical Engineering at UFSC are open until March 16, 2025.
Up to 8 students will be pre-selected according to the notice available at http://brafitec.ufsc.br, with up to 4 places for each of the two projects mentioned in the notice (RAISON and FUTURE – CAPES/BRAFITEC 2025).
The exchange program is scheduled to start in September 2025.
#BRAFITEC #Exchange #LRF #UFSC
Chipus, in partnership with LRF-UFSC (https://lrf.ufsc.br/), is offering a master’s program in microelectronics focused on the development of a high-speed PLL (phase-locked loop) applied to memory interfaces. The master’s student will be supervised by Professor Fernando Rangel de Sousa (LRF-UFSC) and co-supervised by engineers from Chipus.
Interested candidates should send their resume by 29/11/2024 to: jobs@chipus.com.br Email subject: Currículo Mestrado LRF-Chipus.

We are members of the INCT NAMITEC, colaborating in Task A1.4 – Wireless Energy Transfer and Biomedical Applications.
The INCT NAMITEC is a collaborative research network in Electronics aimed at providing innovation to applications in several domains. Its original formation took place in 2001, remaining active until 2016. After a hiatus of 6 years, it was renewed in 2022 in a project approved by CNPq, with an expected duration of 5 years. In the current version, it is formed by 86 main researchers distributed in 8 states, 34 collaborators in the country and 37 collaborators from abroad.
The work methodology focuses on inter-institutional and interdisciplinary collaborations. Activities are organized by related themes.
This work presents a review of the main concepts of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)s and tackles one of their main problems, which is energy consumption. This is done using the data collected by a network deployed at the Hydropower power plant in Cachoeira Dourada. First, an exploratory data analysis of the WSN using statistical and machine learning methods was performed to discover insights about the current state of the network. The analysis provided information about which nodes are more stable, correlations between the data that can be exploited to optimize transmissions, and information about the stability of the links. The work also proposes the use of a Deep Learning model, in a dual prediction scheme, to reduce the transmissions between devices in the network, reduce congestion, and save energy. To do so, a review of data prediction strategies in WSNs is performed. Different neural network based models are introduced and compared using different error metrics in prediction. Finally, a measure of the reduction in data transmission is given, considering different error thresholds. Results show that the model can save a considerable amount of data in transmission, from 70% to 90%, and still maintain a good representation of the measured data.
Tags:
Machine LearningRedes de Sensores sem FiosWireless Sensor Network
The main goal of this work is the development of an open-source software package for steady-state simulation of autonomous circuits using the Harmonic Balance method. Oscillators are autonomous circuits of great interest in radiofrequency applications and a main component of transceivers. The periodic steady-state response of an oscillator is very important to designers, to verify parameters such as oscillating frequency, output power and power consumption. Transient simulations are not efficient to evaluate the periodic steady-state of an oscillator, as a large amount of computation is wasted during the initial startup period. The alternative explored in this work is the usage of the Harmonic Balance method with the Auxiliary Generator Technique to solve directly for the steady-state response of oscillators. To achieve that, a full circuit simulation engine was implemented in the Python programming language, with support to DC, AC, transient and harmonic balance analysis. The circuit netlists are described in code using a simple API. Several device models are available for simulation, such as RLC elements, current and voltage sources, Diode, BJT and MOSFET. Multiple examples are presented and the simulation results are compared to commercial engines to validate the implementations. Advantages of simulating circuits inside a Python environment are presented, involving easiness of data-processing and integration with other libraries
LRF graduate student (André Murilo) participated of the IEEE/MTT-S High Efficiency Power Amplifier Student Design Competition 2021 contest.

Our members and partners keep working hard in pandemic times. We just submitted two papers to I2MTC2021!
Congratulations!
Exploiting the RSSI Long-Term Data of a WSN for the RF Channel Modeling in EPS Environments
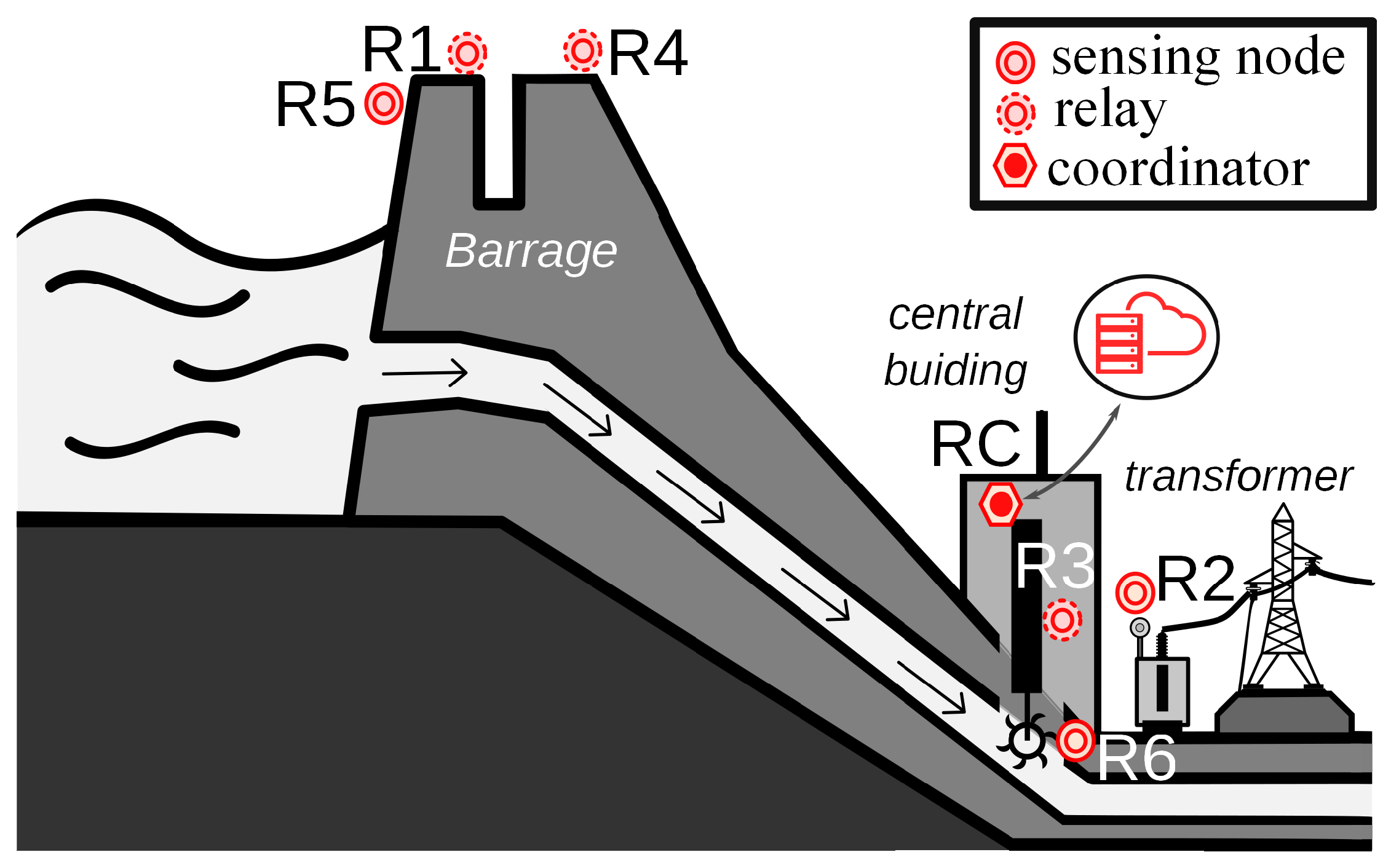
One of the most important challenges in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) is the extension of the sensors lifetime, which are battery-powered devices, through a reduction in energy consumption. Using data prediction to decrease the amount of transmitted data is one of the approaches to solve this problem. This paper provides a comparison of deep learning methods in a dual prediction scheme to reduce transmission. The structures of the models are presented along with their parameters. A comparison of the models is provided using different performance metrics, together with the percent of points transmitted per threshold, and the errors between the final data received by Base Station (BS) and the measured values. The results show that the model with better performance in the dataset was the model with Attention, saving a considerable amount of data in transmission and still maintaining a good representation of the measured data.

Chipless tags for objects identification have been proposed as a low-cost alternative to the well-known chipped Radio Frequency IDentification (RFID) tags technology. More recently, chipless sensors havealso been indicated for specific applications in which RFID-based sensor are not very suitable, such as in harsh environments or ultra-low cost item monitoring. This research have focused on the study of a chipless monitoring system. It was identified that the reading range is one of the most important concerns of these systems, specifically when both the sensor and the reader are size restricted due to a specific application. Consequently, in this work, a new sensor design is proposed to tackle this issue. Several prototypes of the sensor have been implemented in low-cost substrates, such as common PCB glass epoxy-based laminates, and flexible substrates such as plastic and paper. These have shown comparable results to the reported sensors in literature in terms of sensitivity and, more importantly, a superior radar cross section level considering its reduced size. In addition to the sensor, a theoretical analysis and some tests were conducted to prove the need of implementing self-interference cancellation techniques in single-antenna monostatic chipless readers for improving the readability of the tag. Both proposals, on the sensor and on the reader side, can contribute to the reading range enhancement in frequency coded chipless systems.
The MSc. candidate Rafael Licursi successfully defended his thesis, in which he proposed novel Techniques To Locate And Identify Radars With Low Volume, Weight, Costs And Processing Capabilities.
This research proposes signal processing techniques that look at radiofrequency peculiarities in order to soften the processing workload and to allow the design of radar detectors that present low volume, weight, costs and available computational power. Experiments were carried out with a prototype of an Electronic Support Measures (ESM) system with tablet processing, based on Software–Defined Radio (SDR). Results show that the performance of the proposed pulse measurement technique degrades significantly only when the pulse amplitudes are ≤ 3.7 mV at the input of the used SDR. They also show that the suggested direction–finding method presents Gaussian distributions for the measurements, with a standard deviation as high as the lower the amplitude of incoming pulses, which allows, according to the latter, to make inferences about the former. Benefiting from this, the developed pulse–clustering algorithm defined, in front of 6 distributions, clusters of pulses with enclosure rates ≥ 92.71 %. Finally, the results show that the proposed pattern recognition algorithm, when it received a cluster of pulses with patterns of 4 simulated radars, with different types of antenna scan, deinterleaved the 4 patterns, with rates of correct assignment of the pulse repetition interval ≥ 96.30%, besides estimating the pulse repetition interval with errors of the order of 10-5. This study is recommended for the areas of Radar Signal Processing, Direction Finding, Pattern Recognition and Electronic Warfare.
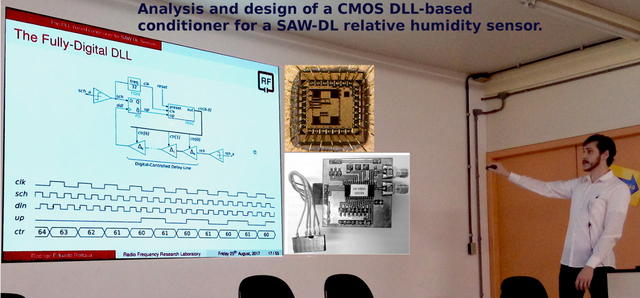
The MSc. candidate Rodrigo Rottava successfully defended his thesis, in which he presented the design and characterization of an integrated circuit to interface a relative humidity SAW sensor.

Work under development at LRF won the third place in the national final of the contest “IDEAS FOR MILK” promoted by EMBRAPA. The project is the result of more than six years of research, involving undergraduate and graduate students. Initially, the focus was on the petroleum extraction sites, where the knowledge of the water-oil fraction during the oil extraction carried relevant information about the well.  A microwave resonant cavity based sensor has been used in this context. More recently, the group started looking for new applications for the sensor, in particular those where there is a correlation between the electrical permittivity and a property of interest. This is the case of milk, where the total of solids (mainly fat) defines the quality of the product and is submitted to specific regulations. Fortunately, we can correlate the amount of total solids (or fat) with the electrical permittivity of the milk using our microwave sensor. For the contest, we proposed to use it to improve the accuracy of the milk production process in real time. The research is conducted by prof. Fernando Rangel and prof. Daniel Pagano, by the PhD students Heron Ávila e Roddy Romero and by the undergraduate student Celso Leite.
A microwave resonant cavity based sensor has been used in this context. More recently, the group started looking for new applications for the sensor, in particular those where there is a correlation between the electrical permittivity and a property of interest. This is the case of milk, where the total of solids (mainly fat) defines the quality of the product and is submitted to specific regulations. Fortunately, we can correlate the amount of total solids (or fat) with the electrical permittivity of the milk using our microwave sensor. For the contest, we proposed to use it to improve the accuracy of the milk production process in real time. The research is conducted by prof. Fernando Rangel and prof. Daniel Pagano, by the PhD students Heron Ávila e Roddy Romero and by the undergraduate student Celso Leite.
This week, our members gathered for the goodbye lunch of our dear colleague Juan Moya.
After recently obtaining his MSc. degree, he is heading back to his mother country Colombia.
We wish him the best in his future endeavours. Good luck Juan!

The MSc. candidate, Juan Moya Baquero, successfully presented his thesis entitled : Miniaturized low-power RFID tag for object identification purposes.


Prof. Wuqiang Yang is visiting us during this week. We are discussing research collaboration in the field of RF/Microwave Instrumentation and Measurement.
Prof. Wuqiang Yang is an IEEE Fellow and he is professor at the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at The University of Manchester, UK.
During his stay he will offer the lecture:
“Current status of industrial tomography and applications of ECT “
Date: 19/09/2016 at 15h30
Place: PGEEL02 – EEL/CTC/UFSC
Further information can be found here.
Our members are now presenting their works at the SBCCI and INSCIT conferences.
More information on the event website.

The paper “Achieving Optimal Efficiency in Energy Transfer to a CMOS Fully-Integrated Wireless Power Receiver,” was accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques. (read it here)

Student Projects 2016: New chips arrived for testing


Several projects were fabricated using the multi-user project from CEITEC (PMUB). We are very proud of having chips delivered by a Brazilian company!

Prof. Rangel visited The University of Manchester between 11/2015 and 02/2016. There he worked designing resonant cavity sensors at the Industrial process tomography (IPT). At Manchester, Prof. Rangel was hosted by Prof. Wuqiang Yang.
Our group has opened a Posdoc position. Any interested candidate on working with RFID/ SDR transceivers and related subjects may contact us through our opportunities page.
Our PhD. student, Arturo Fajardo, presented four papers in the last edition of LASCAS / IBERCHIP, last February in Florianópolis – Brazil. These works are related to energy and power management in WBAN sensor nodes. Read the articles and presentation slides on our publications page.
 Applications for the sandwich undergraduate program in France for students of Electronics Engineering and Electrical Engineering at UFSC are open until March 16, 2025.
Applications for the sandwich undergraduate program in France for students of Electronics Engineering and Electrical Engineering at UFSC are open until March 16, 2025.











 A microwave resonant cavity based sensor has been used in this context. More recently, the group started looking for new applications for the sensor, in particular those where there is a correlation between the electrical permittivity and a property of interest. This is the case of milk, where the total of solids (mainly fat) defines the quality of the product and is submitted to specific regulations. Fortunately, we can correlate the amount of total solids (or fat) with the electrical permittivity of the milk using our microwave sensor. For the contest, we proposed to use it to improve the accuracy of the milk production process in real time. The research is conducted by prof. Fernando Rangel and prof. Daniel Pagano, by the PhD students Heron Ávila e Roddy Romero and by the undergraduate student Celso Leite.
A microwave resonant cavity based sensor has been used in this context. More recently, the group started looking for new applications for the sensor, in particular those where there is a correlation between the electrical permittivity and a property of interest. This is the case of milk, where the total of solids (mainly fat) defines the quality of the product and is submitted to specific regulations. Fortunately, we can correlate the amount of total solids (or fat) with the electrical permittivity of the milk using our microwave sensor. For the contest, we proposed to use it to improve the accuracy of the milk production process in real time. The research is conducted by prof. Fernando Rangel and prof. Daniel Pagano, by the PhD students Heron Ávila e Roddy Romero and by the undergraduate student Celso Leite.











